
Github: of_scan_flat_dt
Email: BuddyZhang1 buddy.zhang@aliyun.com
目录
源码分析
of_scan_flat_dt
of_scan_flat_dt
|
|---fdt_next_node
|
|---fdt_get_name
|
|---it函数作用:启动阶段,遍历 DTB 中所有的节点
/**
* of_scan_flat_dt - scan flattened tree blob and call callback on each.
* @it: callback function
* @data: context data pointer
*
* This function is used to scan the flattened device-tree, it is
* used to extract the memory information at boot before we can
* unflatten the tree
*/
int __init of_scan_flat_dt(int (*it)(unsigned long node,
const char *uname, int depth,
void *data),
void *data)
{
const void *blob = initial_boot_params;
const char *pathp;
int offset, rc = 0, depth = -1;
for (offset = fdt_next_node(blob, -1, &depth);
offset >= 0 && depth >= 0 && !rc;
offset = fdt_next_node(blob, offset, &depth)) {
pathp = fdt_get_name(blob, offset, NULL);
if (*pathp == '/')
pathp = kbasename(pathp);
rc = it(offset, pathp, depth, data);
}
return rc;
}函数的作用就是从 DTB 中,遍历所有的节点,然后将节点的名字,节点在 DTB device-tree structure 域中的偏移,嵌套深度,和私有数据传递给传入的 it(…) 函数。
函数首先调用 fdt_next_node() 函数获得 DTB device-tree structure 域的第一个节 点,只要每个 device-tree structure 在 DTB device-tree structure 域的偏移值 offset 大于零,depth 不为负数,rc 一直为零,那么 for 循环就一直循环下去,通过 调用 fdt_next_node() 函数获得下一个节点。在每次循环中,函数调用 fdt_get_name() 获得节点的名字,然后将节点的名字,节点在 DTB device-tree structure 域中的偏移, 嵌套深度,和私有数据传递给传入的 it(…) 函数。it(…) 函数为传入的参数,所以 可以通过这个函数遍历所有的节点。
fd_next_node
int fdt_next_node(const void *fdt, int offset, int *depth)
{
int nextoffset = 0;
uint32_t tag;
if (offset >= 0)
if ((nextoffset = _fdt_check_node_offset(fdt, offset)) < 0)
return nextoffset;
do {
offset = nextoffset;
tag = fdt_next_tag(fdt, offset, &nextoffset);
switch (tag) {
case FDT_PROP:
case FDT_NOP:
break;
case FDT_BEGIN_NODE:
if (depth)
(*depth)++;
break;
case FDT_END_NODE:
if (depth && ((--(*depth)) < 0))
return nextoffset;
break;
case FDT_END:
if ((nextoffset >= 0)
|| ((nextoffset == -FDT_ERR_TRUNCATED) && !depth))
return -FDT_ERR_NOTFOUND;
else
return nextoffset;
}
} while (tag != FDT_BEGIN_NODE);
return offset;
}函数用于获得当前 device-tree structure 节点之后的下一个 device-tree structure 节点。
参数 fdt 指向一个可用的 DTB 所在的虚拟地址,offset 为当前 device-tree structure 在 DTB device-tree structure 段的偏移,depth 变量用于存储节点深度。
函数首先检测 offset 是否大于零,以此判断当前 device-tree structure 是不是节点。 如果大于零,那么当前 device-tree structure 就是一个节点,直接调用 _fdt_check_node_offset() 函数获得下一个可用的节点偏移,如果函数返回值小于零, 直接错误返回,表示当前 device-tree structure 不是节点或无法获得下一个 device-tree structure。然后函数从下一个 device-tree structure 开始遍历当前节 点的属性或子节点。首先调用 fdt_next_tag() 函数获得下一个 device-tree strucure 对于的 tag 值。对于 tag 值,如果 tag 为 FDT_BEGIN_NODE,那么认为下一个 device-tree structure 是一个子节点,depth 不为零的时候加一;如果 tag 为 FDT_END_NODE,并且 depth 不为零,表示现在在子节点内,如果 depth 减一之后小于 零,那么下一个 device-tree structure 是一个完整的 node,直接返回其 offset;如 果 tag 为 FDT_END,并且下一个 device-tree structure 的偏移不为负数,且 depth 不为零,即嵌套,那么这是一个完整的节点,所以返回 offset;其余情况均不符合要求。 循环直到下一个 FDT_BEGIN_NODE 结束。
fdt_get_name
const char *fdt_get_name(const void *fdt, int nodeoffset, int *len)
{
const struct fdt_node_header *nh = _fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, nodeoffset);
int err;
if (((err = fdt_check_header(fdt)) != 0)
|| ((err = _fdt_check_node_offset(fdt, nodeoffset)) < 0))
goto fail;
if (len)
*len = strlen(nh->name);
return nh->name;
fail:
if (len)
*len = err;
return NULL;
}该函数用于获得 device-tree structure 的名字。
参数 fdt 指向一个可用 DTB 的虚拟地址;nodeoffset 参数指定了 device-tree structure 在 DTB device-tree structure 域的偏移;len 参数用于存储名字的长度。
函数首先调用 _fdt_offset_ptr() 函数获得 nodeoffset 指定的 device-tree structure 的虚拟地址。然后调用 fdt_check_header() 函数检查 DTB header 的有效性,并且通过 调用 _fdt_check_node_offset() 函数确定这个 device-tree structure 是一个节点。 经过以上两个检查之后就可以驱动这个 device-tree structure 符合要求,然后将节点 的名字的长度存储到 len 参数里,最后直接返回节点的字符串。
kbasename
/**
* kbasename - return the last part of a pathname.
*
* @path: path to extract the filename from.
*/
static inline const char *kbasename(const char *path)
{
const char *tail = strrchr(path, '/');
return tail ? tail + 1 : path;
}这个函数用于返回路径字符串中,最后部分的字符串。例如 “/arch/arm64/boot/dts”, 将这个字符串传递给 kbasename() 之后,函数返回 “dts”.
_fdt_check_node_offset
int _fdt_check_node_offset(const void *fdt, int offset)
{
if ((offset < 0) || (offset % FDT_TAGSIZE)
|| (fdt_next_tag(fdt, offset, &offset) != FDT_BEGIN_NODE))
return -FDT_ERR_BADOFFSET;
return offset;
}_fdt_check_node_offset() 函数用于判断一个 device-tree structure 是不是一个节点。
参数 fdt 指向 DTB 的虚拟地址,offset 表示 device-tree structure 在 DTB device-tree structure 段中的偏移
这个函数对 offset 进行检测,如果 offset 小于 0 或 offset 没有按 FDT_TAGSIZE 对 齐,或者 device-tree structure 不是一个节点,那么判定 offset 是一个 FDT_ERR_BADOFFSET; 如果 device-tree structure 是一个节点,并将 offset 的值设置 为当前 device-tree structure 的下一个 device-tree structure。
_fdt_check_prop_offset
int _fdt_check_prop_offset(const void *fdt, int offset)
{
if ((offset < 0) || (offset % FDT_TAGSIZE)
|| (fdt_next_tag(fdt, offset, &offset) != FDT_PROP))
return -FDT_ERR_BADOFFSET;
return offset;
}_fdt_check_prop_offset() 函数用于查看 offset 对应的 device-tree structure 是不 是一个属性,如果是则返回下一个 device-tree structure 在 DTB device-tree structure 段中的偏移。
fdt_next_tag
uint32_t fdt_next_tag(const void *fdt, int startoffset, int *nextoffset)
{
const uint32_t *tagp, *lenp;
uint32_t tag;
int offset = startoffset;
const char *p;
*nextoffset = -FDT_ERR_TRUNCATED;
tagp = fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, offset, FDT_TAGSIZE);
if (!tagp)
return FDT_END; /* premature end */
tag = fdt32_to_cpu(*tagp);
offset += FDT_TAGSIZE;
*nextoffset = -FDT_ERR_BADSTRUCTURE;
switch (tag) {
case FDT_BEGIN_NODE:
/* skip name */
do {
p = fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, offset++, 1);
} while (p && (*p != '\0'));
if (!p)
return FDT_END; /* premature end */
break;
case FDT_PROP:
lenp = fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, offset, sizeof(*lenp));
if (!lenp)
return FDT_END; /* premature end */
/* skip-name offset, length and value */
offset += sizeof(struct fdt_property) - FDT_TAGSIZE
+ fdt32_to_cpu(*lenp);
break;
case FDT_END:
case FDT_END_NODE:
case FDT_NOP:
break;
default:
return FDT_END;
}
if (!fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, startoffset, offset - startoffset))
return FDT_END; /* premature end */
*nextoffset = FDT_TAGALIGN(offset);
return tag;
}fdt_next_tag() 函数主要用于获得 offset 指定的 device-tree structure 的虚拟地址, 以及下一个 device-tree structure 在 device-tree structure 段中偏移。startoff 参数表示当前 device-tree structure 在 device-tree structure 段中的偏移,fdt 参 数表示一个可用的 DTB 虚拟地址。
fdt_next_tag() 函数首先通过传入参数 startoffset 和 fdt 到 fdt_offfset_ptr() 函 数,以此获得一个 device-tree structure 的虚拟地址。如果获得的虚拟地址为 NULL, 那么内核认为未找到期望的 device-tree structure,所以直接返回 FDT_END,代表查找 过早结束,并且将下一个 device-tree structure 在 device-tree structure 段中的偏 移标识为 -FDT_ERR_TRUNCATED, 以此表示 DTB 被截断了。接下来通过 fdt32_to_cpu() 函数,将 device-tree structure 的虚拟地址转换为符合平台大小端的数据结构,存储 在 tag 变量里,然后将 offset 增加 FDT_TAGSIZE,以此指向 device-tree structure 的第二个成员。在获得 device-tree structure 首地址之后,对 device-tree structure 第一个字节也就是 tag 进行判断,看其是否属于节点还是属性,以下是一个 device-tree structure 的基本结构:
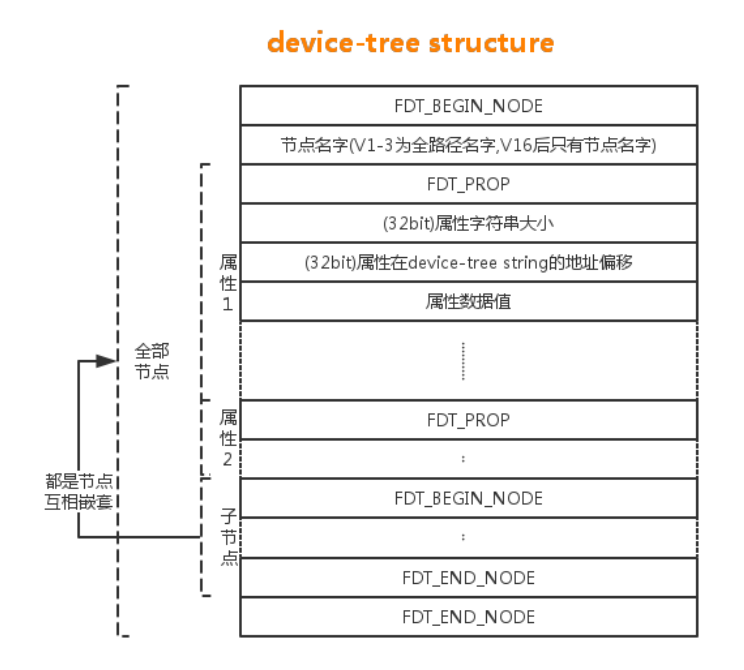
如果 device-tree structure 的 tag 是 FDT_BEGIN_NODE,那么 device-tree structure 就是一个独立的节点或子节点;如果 device-tree structure 的首地址是 FDT_PROP,那么节点就是一个属性描述;如果 device-tree structure 首地址是 FDT_END, FDT_END_NODE, FDT_NOP 则忽略。
如果 device-tree structure 是一个节点,又根据节点的定义可知:
struct fdt_node_header {
uint32_t tag;
char name[0];
};此时,内核通过使用 while 循环将跳过 name 域,代码如下:
case FDT_BEGIN_NODE:
/* skip name */
do {
p = fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, offset++, 1);
} while (p && (*p != '\0'));
if (!p)
return FDT_END; /* premature end */
break;通过上面的代码,struct fdt_node_header 结构中的 name 成员将被跳过,这样就可以 找到下一个 device-tree structure 的首地址。如果 device-tree structure 是一个 属性,属性的定义如下:
struct fdt_property {
uint32_t tag;
uint32_t len;
uint32_t nameoff;
char data[0];
};对于 device-tree structure 是一个属性,内核的处理如下:
case FDT_PROP:
lenp = fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, offset, sizeof(*lenp));
if (!lenp)
return FDT_END; /* premature end */
/* skip-name offset, length and value */
offset += sizeof(struct fdt_property) - FDT_TAGSIZE
+ fdt32_to_cpu(*lenp);
break;首先通过 fdt_offset_ptr() 函数获得属性的长度值后,跳过了属性的 nameoff,len, 和 data 成员。通过上面的处理之后,内核已经计算出下一个 device-tree structure 相对于当前 device-tree structure 之间的偏移,然后调用 fdt_offset_ptr() 获得下 一个 device-tree structure 的虚拟地址,以此判断下一个 device-tree structure 是否存在,如果不存在则返回 FDT_END;如果下一个 device-tree structure 的虚拟地 址存在,那么内核将下一个 device-tree structure 在 DTB device-tree structure 段 中的偏移赋值给 netoffset 指针。代码如下:
if (!fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, startoffset, offset - startoffset))
return FDT_END; /* premature end */
*nextoffset = FDT_TAGALIGN(offset);
return tag;因此,fdt_next_tag() 函数通过 DTB 的虚拟地址,以及 device-tree structure 在 device-tree structure 段中的偏移可以获得 device-tree structure 的虚拟地址以及 下一个 device-tree structure 在 device-tree structure 段中的偏移。
fdt_offset_ptr
const void *fdt_offset_ptr(const void *fdt, int offset, unsigned int len)
{
const char *p;
if (fdt_version(fdt) >= 0x11)
if (((offset + len) < offset)
|| ((offset + len) > fdt_size_dt_struct(fdt)))
return NULL;
p = _fdt_offset_ptr(fdt, offset);
if (p + len < p)
return NULL;
return p;
}这个函数主要做一些基本检测之后,返回节点的虚拟地址。本函数中,传入参数 fdt 指 向一个可用的 DTB,offset 参数指定了节点在 DTB device-tree structure 段中的偏 移,len 参数指定了节点长度。函数首先检查 DTB 的 version 是否符合特定要求,如 果 version 大于 0x10,且节点在 device-tree structure 段中的空间超出了 device-tree structure 的空间,那么这是一个错误的情况,不能返回指定节点的虚拟地 址,直接返回 NULL。如果前面的检测没有问题,那么函数调用 _fdt_offset_ptr() 去获 得节点的虚拟地址。在获得节点虚拟地址之后,如果节点的虚拟加上其长度小于虚拟地址, 这是一种错误的越界问题,所以也返回 NULL。待上面的检测都通过之后,就直返回节点 的虚拟地址。
_fdt_offset_ptr
static inline const void *_fdt_offset_ptr(const void *fdt, int offset)
{
return (const char *)fdt + fdt_off_dt_struct(fdt) + offset;
}在这个函数中,fdt 指向一个可用的 DTB 的虚拟地址,offset 参数指定了节点在 DTB 的 device-tree structure 段中的偏移。通过这个函数,可以获得节点的虚拟地址,其 他程序就可以通过这个地址直接访问节点。
fdt_version
#define fdt_version(fdt) (fdt_get_header(fdt, version))通过这个函数,从 DTB header 中获得 version 域信息。
fdt_size_dt_struct
#define fdt_size_dt_struct(fdt) (fdt_get_header(fdt, size_dt_struct))这个函数通过调用 fdt_get_header() 从 DTB header 中获得 device-tree structure 的大小。
fdt_get_header
#define fdt_get_header(fdt, field) \
(fdt32_to_cpu(((const struct fdt_header *)(fdt))->field))该函数用于从 DTB header 中读取指定的域。并按指定的大小端进行变换。
函数实践
实践目的是在 DTS 文件中构建一个私有节点,私有节点包含了一个子节点,子节点又包 含了一个子节点。然后在驱动中通过 of_scan_flat_dt() 函数来遍历这三种节点。函数 的定义如下:
int __init of_scan_flat_dt(int (*it)(unsigned long node, const char *uname, int depth, void *data), void *data);这个函数经常用用于遍历指定节点及其附属的子节点,驱动中,可以通过 uname 作为关 键字来过滤需要的节点。
本文实践基于 Linux 4.20.8 arm32 平台,开发者可以参考如下文章快速搭建一个 调试环境:
DTS 文件
由于使用的平台是 ARM32,所以在源码 /arch/arm/boot/dts 目录下创建一个 DTSI 文件,一个节点包含子节点,子节点又包含子节点。具体内容如下:
/*
* DTS Demo Code
*
* (C) 2019.01.06 <buddy.zhang@aliyun.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*/
/ {
DTS_demo {
compatible = "DTS_demo, BiscuitOS";
status = "okay";
DTS_demo_sub0 {
sub_level = <0x1>;
DTS_demo_sub1 {
sub_level = <0x2>;
};
};
};
};创建完毕之后,将其保存并命名为 DTS_demo.dtsi。然后开发者在 Linux 4.20.8 的源 码中,找到 arch/arm/boot/dts/vexpress-v2p-ca9.dts 文件,然后在文件开始地方添 加如下内容:
#include "DTS_demo.dtsi"编写 DTS 对应驱动
准备好 DTSI 文件之后,开发者编写一个简单的驱动,这个驱动作为 DTS_demo 的设备 驱动,在 DTS 机制遍历时会调用匹配成功的驱动,最终运行驱动里面的代码。驱动编写 如下:
/*
* DTS:
* of_get_flat_dt_root()
* of_get_flat_dt_prop()
*
* (C) 2018.11.14 <buddy.zhang@aliyun.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*/
/*
* Private DTS file: DTS_demo.dtsi
*
* / {
* DTS_demo {
* compatible = "DTS_demo, BiscuitOS";
* status = "okay";
* DTS_demo_sub0 {
* sub_level = <0x1>;
*
* DTS_demo_sub1 {
* sub_level = <0x2>;
* };
* };
* };
* };
*
* On Core dtsi:
*
* include "DTS_demo.dtsi"
*/
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/of_platform.h>
#include <linux/of_fdt.h>
/* define name for device and driver */
#define DEV_NAME "DTS_demo"
/* Parse specify device-tree structure node */
static int DTS_demo_dt_scan_node(unsigned long node, const char *uname,
int depth, void *data)
{
/* Filter father node */
if ((depth == 1) && (strcmp(uname, "DTS_demo") == 0)) {
printk("Father node: %s\n", uname);
} else if ((depth == 2) && (strcmp(uname, "DTS_demo_sub0") == 0)) {
/* Sub-level 1 Child node */
printk("Sub-0 node: %s\n", uname);
} else if ((depth == 3) && (strcmp(uname, "DTS_demo_sub1") == 0 )) {
/* Sub-level 2 Child node */
printk("Sub-1 node: %s\n", uname);
}
return 0;
}
/* probe platform driver */
static int DTS_demo_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct device_node *np = pdev->dev.of_node;
unsigned long dt_root;
unsigned int *dt_int;
const char *dt_char;
printk("DTS demo probe entence\n");
/* Rettrieve various infomation from the all node */
of_scan_flat_dt(DTS_demo_dt_scan_node, NULL);
return 0;
}
/* remove platform driver */
static int DTS_demo_remove(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
return 0;
}
static const struct of_device_id DTS_demo_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "DTS_demo, BiscuitOS", },
{ },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, DTS_demo_of_match);
/* platform driver information */
static struct platform_driver DTS_demo_driver = {
.probe = DTS_demo_probe,
.remove = DTS_demo_remove,
.driver = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.name = DEV_NAME, /* Same as device name */
.of_match_table = DTS_demo_of_match,
},
};
module_platform_driver(DTS_demo_driver);编写好驱动之后,将其编译进内核。编译内核和 dts,如下命令:
make ARCH=arm BiscuitOS/output/linux-4.20.8/arm-linux-gnueabi/arm-linux-gnueabi/bin/arm-linux-gnueabi- j8
make ARCH=arm BiscuitOS/output/linux-4.20.8/arm-linux-gnueabi/arm-linux-gnueabi/bin/arm-linux-gnueabi- dtbs启动内核,在启动阶段就会运行驱动的 probe 函数,并打印如下信息:
[ 3.553142] io scheduler cfg registered (default)\
[ 3.553439] DTS demo probe entence
[ 3.553443] Father node: DTS_demo
[ 3.553449] Sub-0 node: DTS_demo_sub0
[ 3.553449] Sub-1 node: DTS_demo_sub1驱动中,自定义了一个函数 DTS_demo_dt_scan_node(), 函数主要作用是从 DTB 中找出 指定的节点,节点的子节点,和子节点的子节点。of_scan_flat_dt() 函数遍历 DTB 中 所有的节点。